Harry Morgan
6878
26581
773
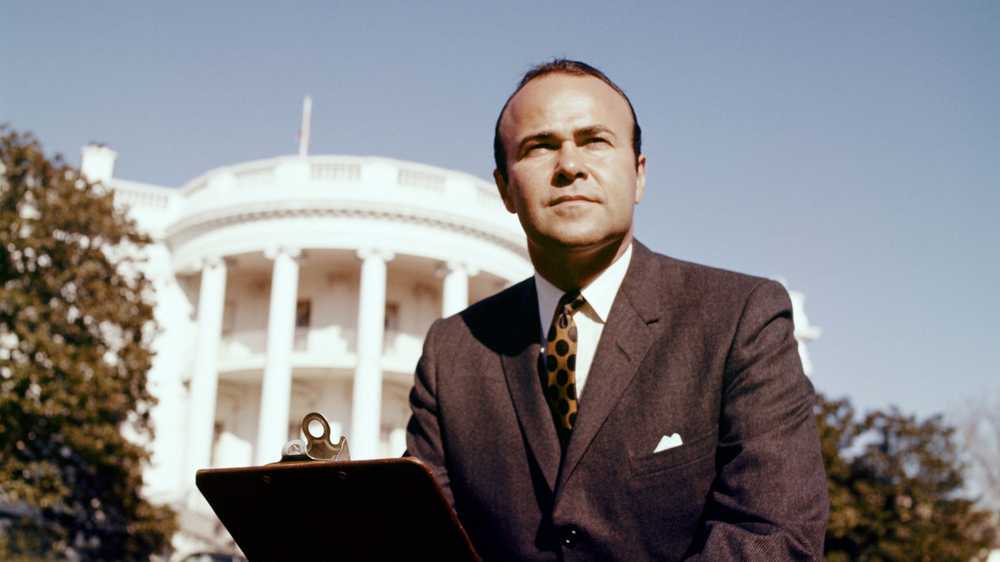
Waar geschiedenis werd geschreven, was Sander Vanocur daar vaak met de hardnekkige vragen. De baanbrekende journalist die meer dan 40 jaar lang politiek behandelde voor televisie en print, stierf aan complicaties door dementie op maandag 16 september 2019, terwijl hij in de hospice-zorg in Santa Barbara, Californië, volgens De New York Times. Hij was 91.
Vanocur was een van de vier journalisten in het panel van het eerste op televisie uitgezonden presidentiële debat tussen Richard Nixon en John F. Kennedy, bekeken door 70 miljoen kijkers in 1960. Meer dan drie decennia later was hij een van de panelleden voor het debat tussen George HW Bush, Bill Clinton en Ross Perot in 1992.
Hij organiseerde ook twee series over de GESCHIEDENIS, Films op tijd en Geschiedenis & # x2019; s Business. Voor Films op tijd, hij interviewde ooit Oliver Stone en Anthony Hopkins over de film uit 1995 Nixon, waarbij de afbeeldingen van de film worden vergeleken met de werkelijke historische gebeurtenissen. & # x201C; It & # x2019; s in het oog van de toeschouwer, & # x201D; Vanocur vertelde de Los Angeles Times van zijn nauwkeurigheid. & # x201C; Een deel van mij rebelleert tegen losheid met de feiten. Het andere deel zegt dat mensen het recht hebben om geschiedenis op hun eigen manier te interpreteren ... Ik denk dat hij zijn opvattingen uitzet en in de film zet, wat zijn recht is. Maar is het een accurate geschiedenis? Ik denk het niet & # x2019; t denk ik. & # X201D;
Hij zelf verscheen ook in films als een journalist, met optredens in 1971 & # x2019; s The Gang That Couldn & # x2019; t Rechte shoot, 1980 & # x2019; s Til de Titanic op, 1993 & # x2019; s Dave, 1996 & # x2019; s Wegkomen met moord en 1994 & # x2019; s Zonder waarschuwing.Hij ontving ook de E.W. Scripps School of Journalism & # x2019; s Carr Van Anda Award.
Geboren op 8 januari 1928 in Cleveland, heette zijn naam oorspronkelijk Sander Vinocur. Maar nadat zijn moeder en zijn advocaatvader gescheiden waren, verhuisde ze met haar kinderen naar Peoria, Illinois, en veranderde de spelling van hun achternaam in Vanocur omdat ze & # x201C; boos was op de oude man, & # x201D; als De New York Times zegt Vanocur vertelde de krant St. Petersburg, Florida, De avond onafhankelijk.
Vanocur studeerde af aan de Western Military Academy in Alton, Illinois en Northwestern University, en studeerde ook aan de London School of Economics. Hij diende ook in het leger.
Hij begon zijn carrière als verslaggever voor De Manchester Guardian en werkte voor de BBC en CBS News, voordat ze naar De New York Times in 1955. In 1957 verhuisde hij naar NBC News waar hij verschillende functies vervulde als correspondent voor het Witte Huis, Vandaag toon D.C.-correspondent, De Huntley-Brinkley-rapport bijdragende redacteur en Eerste dinsdag gastheer. In de vroege jaren 1970 verliet hij NBC voor PBS, gevolgd door stints bij De Washington Post van 1975 tot 1977 en ABC News van 1977 tot 1991.
Een van zijn meest opvallende interviews waren het praten met Martin Luther King, Jr., in de Ebenezer Baptist Church minder dan een jaar voordat hij werd vermoord en Robert Kennedy in Los Angeles in het Ambassador Hotel, net voordat Kennedy werd vermoord in 1968.
& # x201C; I & # x2019; ben een groot voorstander van de persvrijheid & # x2014; zolang ze iets te zeggen hebben, & # x201D; hij zei in 2004 in een toespraak van Stanford University.
Vanocur was ook consultant bij het Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions, professor communicatie aan de Duke University, professional-in-residence bij The Freedom Forum in Arlington, Virginia, en had zijn eigen communicatieconsultancybedrijf, Old Owl Communications.
Hij was getrouwd met Edith Pick in 1956 en had twee zonen, Christoper en Nicholas. Nadat Pick in 1975 stierf, trouwde hij met Virginia Backus Vancour, die hem overleeft. Hij & # x2019; s overleefde ook door een stiefdochter, Daphne Wood Hicks.
MEER VERHALEN VAN BIOGRAFIE
 Nieuws
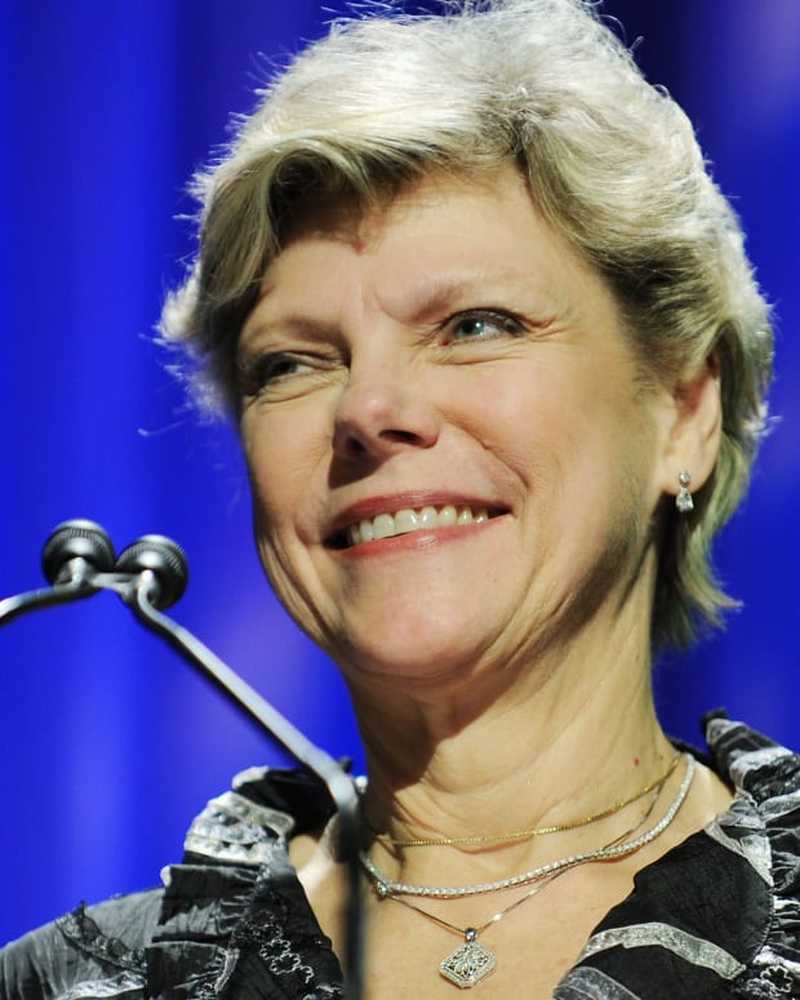
NieuwsCokie Roberts, politiek journalist en bestsellerauteur, sterft op 75-jarige leeftijd
Cokie Roberts, politiek journalist en bestsellerauteur, sterft op 75-jarige leeftijd
- Door Rachel Chang, 17 september 2019
 In het nieuws
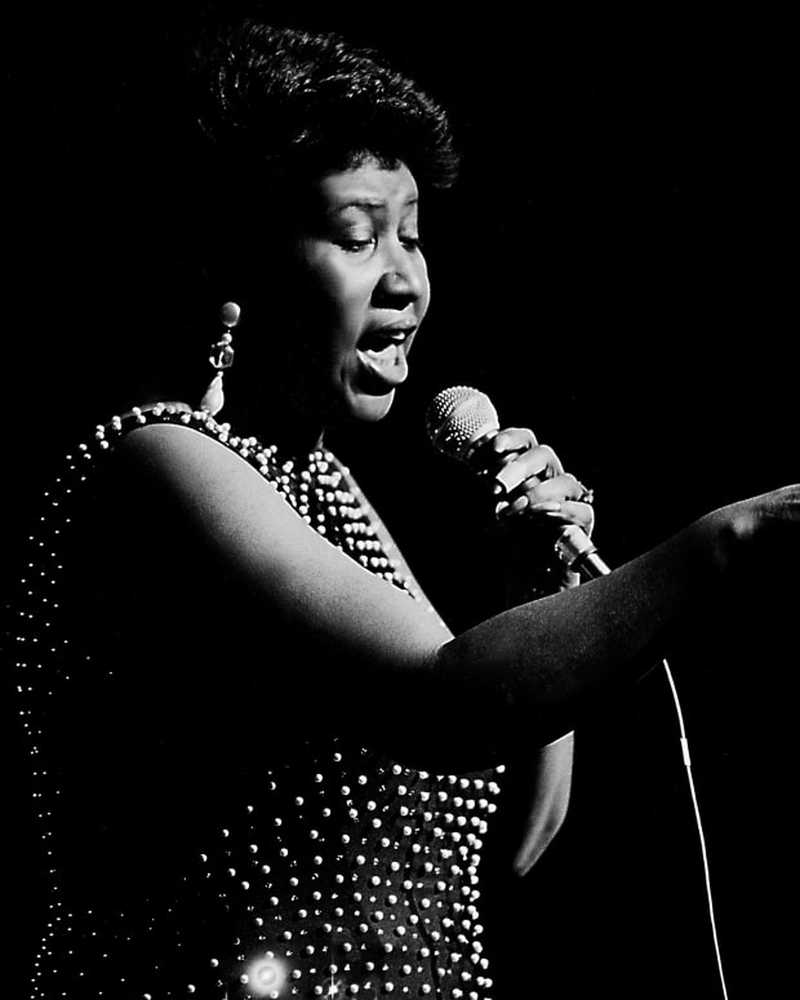
In het nieuwsAretha Franklin sterft op 76-jarige leeftijd
De "Queen of Soul" laat een record achter van meer dan 20 top R&B hits en 18 Grammy-overwinningen.
- Door David Blatty 16 juni 2019
 In het nieuws
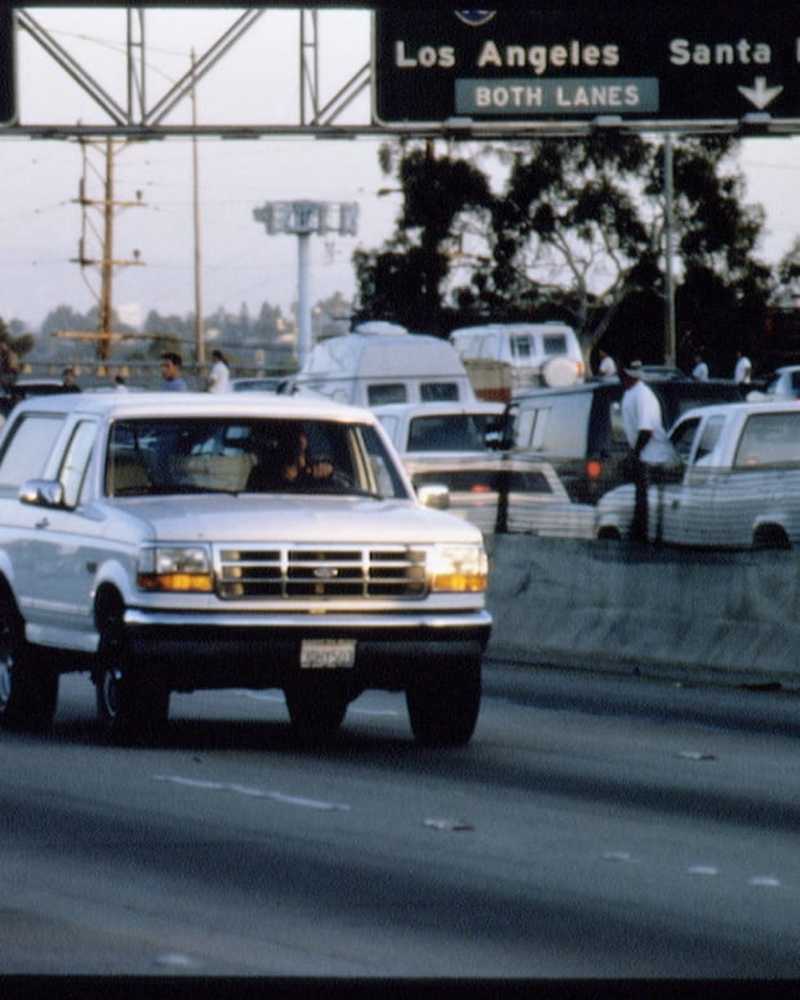
In het nieuwsO.J. Simpson's Freeway Chase: wat er met de White Ford Bronco is gebeurd
Meer dan twee decennia sinds de achtervolging met lage snelheid van de moord verdachte, zit de beruchte auto in een misdaadmuseum in Tennessee.
- Door Rachel Chang 17 juni 2019
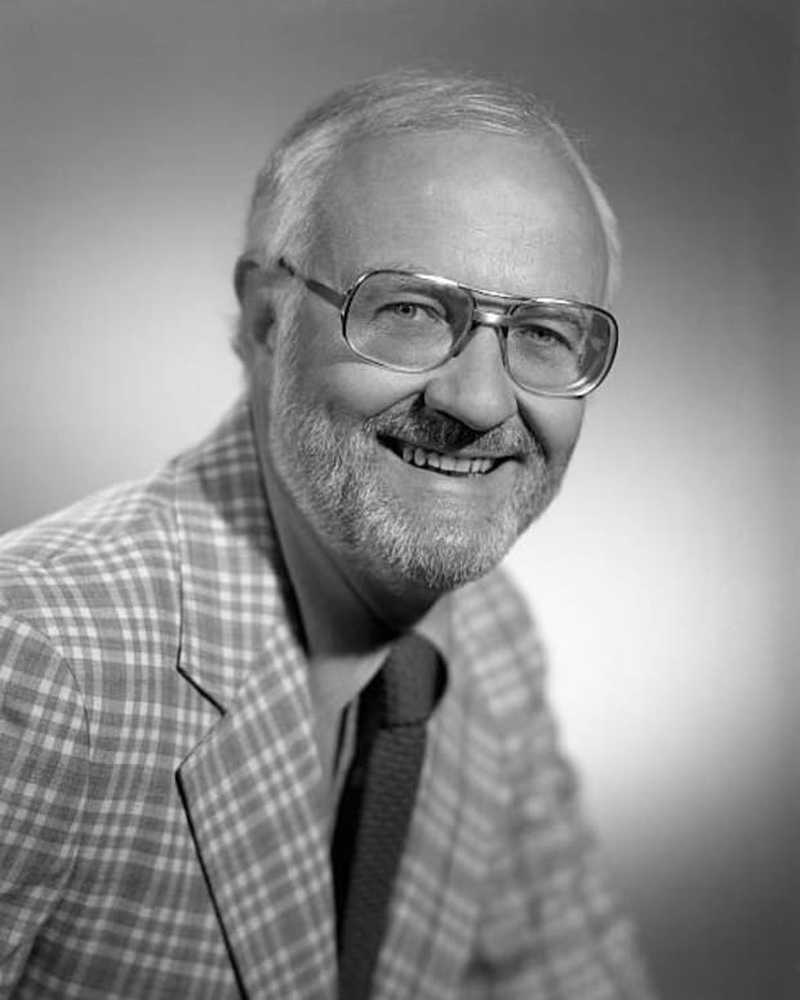 Beroemdheid
BeroemdheidJack Perkins, 'Biography' Host, sterft op 85
De verslaggever en commentator presenteerden de reeks van 1994-1999.
- Door Eudie Pak 21 augustus 2019
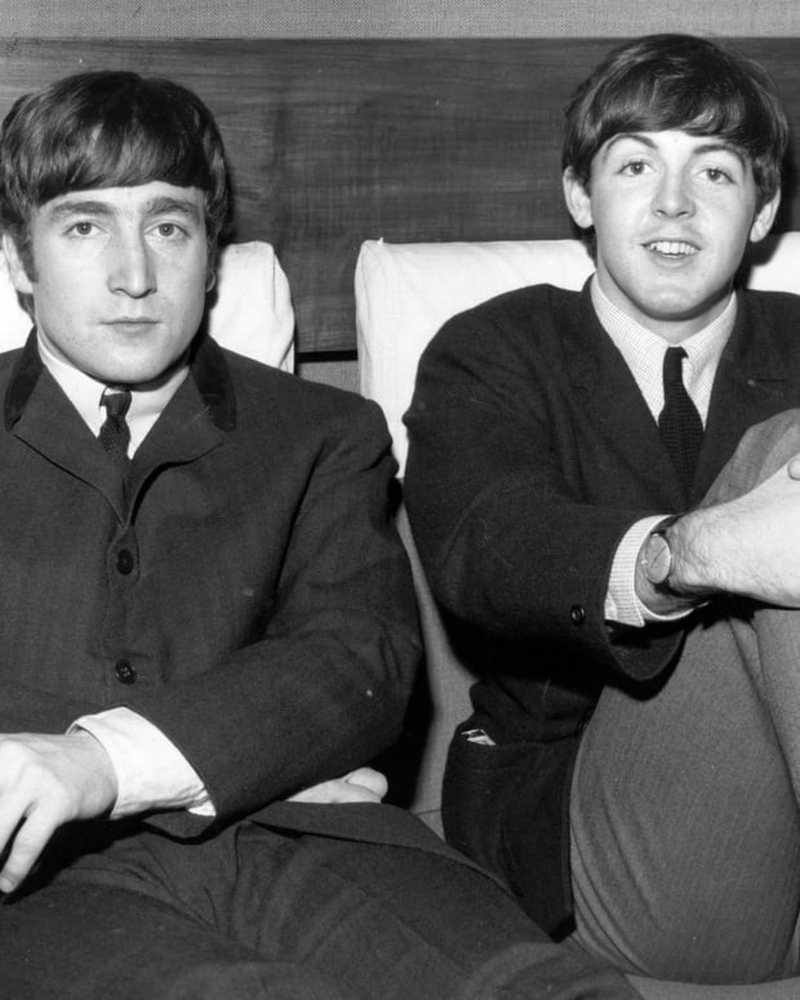 Beroemdheid
BeroemdheidInside 'Lreplaceable' Bond van John Lennon en Paul McCartney - en Epic Fall Out
Happenstance bracht een van de meest levendige vriendschappen in de muziekgeschiedenis samen. Maar spanning dwong The Beatles-bandleden uit elkaar - totdat ze hoorden dat ze het gewoon moesten laten.
- Door Rachel Chang 24 september 2019
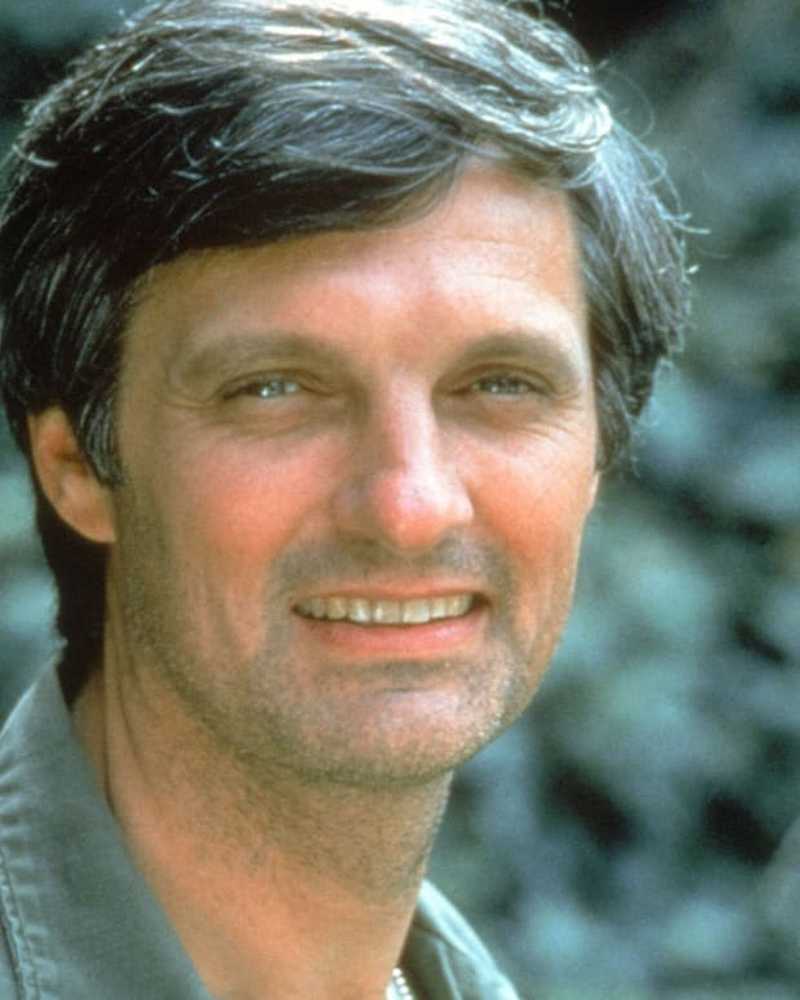 Nostalgie
NostalgieTV-sterren die de jaren 70 regeerden
Alan Alda wordt vandaag 80. Om de geliefde acteur te vieren, kijken we terug op zijn heerschappij als een iconische tv-ster uit de jaren 70 met een spotlight op enkele andere beroemdheden die ook het decennium regeerden.
- Door Laurie Ulster 24 juni 2019
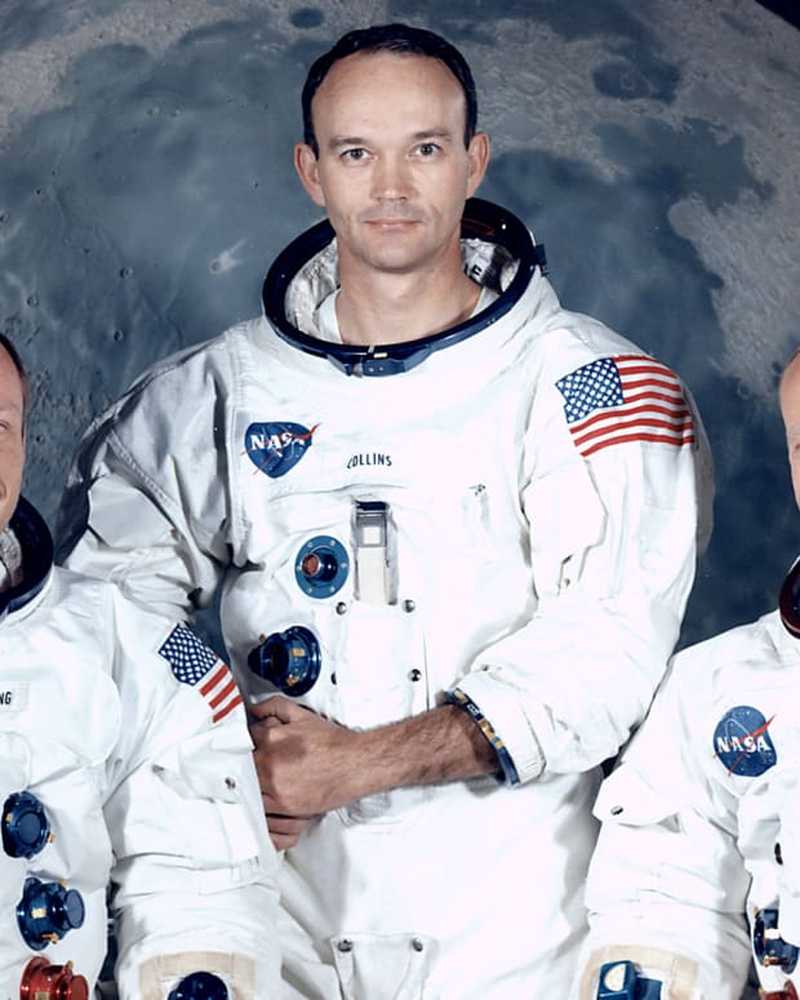 Geschiedenis en cultuur
Geschiedenis en cultuurHoe Neil Armstrong en Buzz Aldrin werden geselecteerd voor de Apollo 11-missie
Vlucht geobsedeerd sinds de kindertijd, bundelden de Koreaanse oorlogsveteranen hun krachten in een van de meest succesvolle ruimtemissies ooit, de maanwandeling van 1969.
- Door Rachel Chang, 20 juli 2019
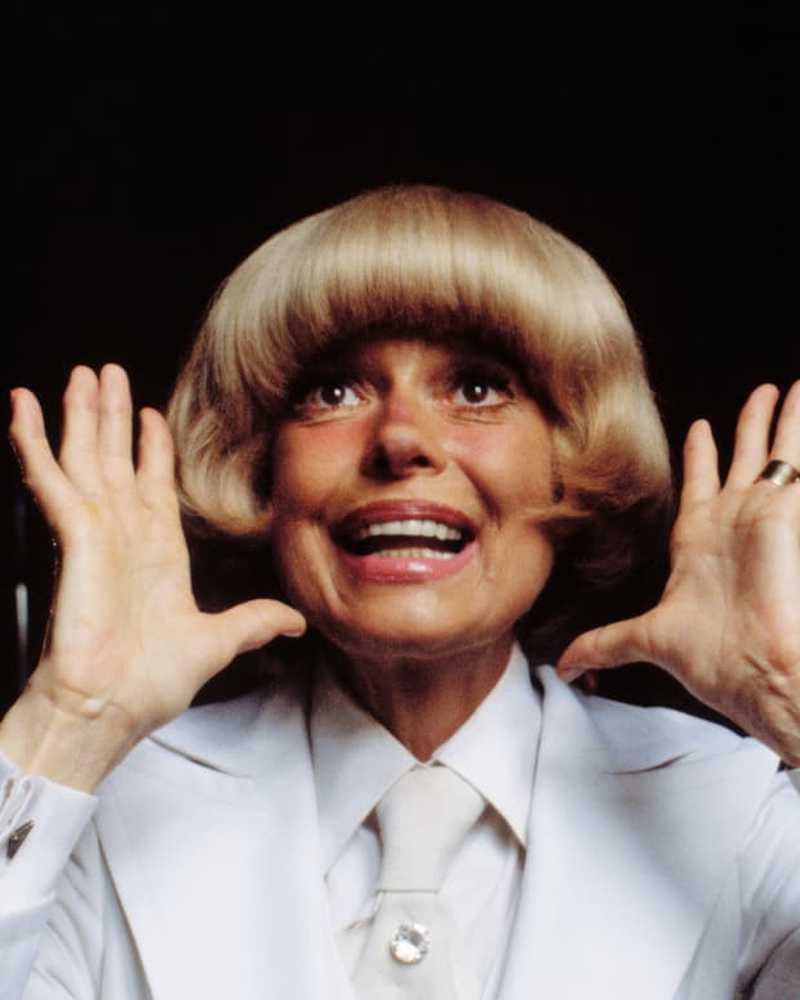 In het nieuws
In het nieuwsCarol Channing, Broadway's Geliefde Dolly en Lorelei, sterft op 97
De performer stierf in haar huis in Californië.
- Door David Sheward 17 juni 2019
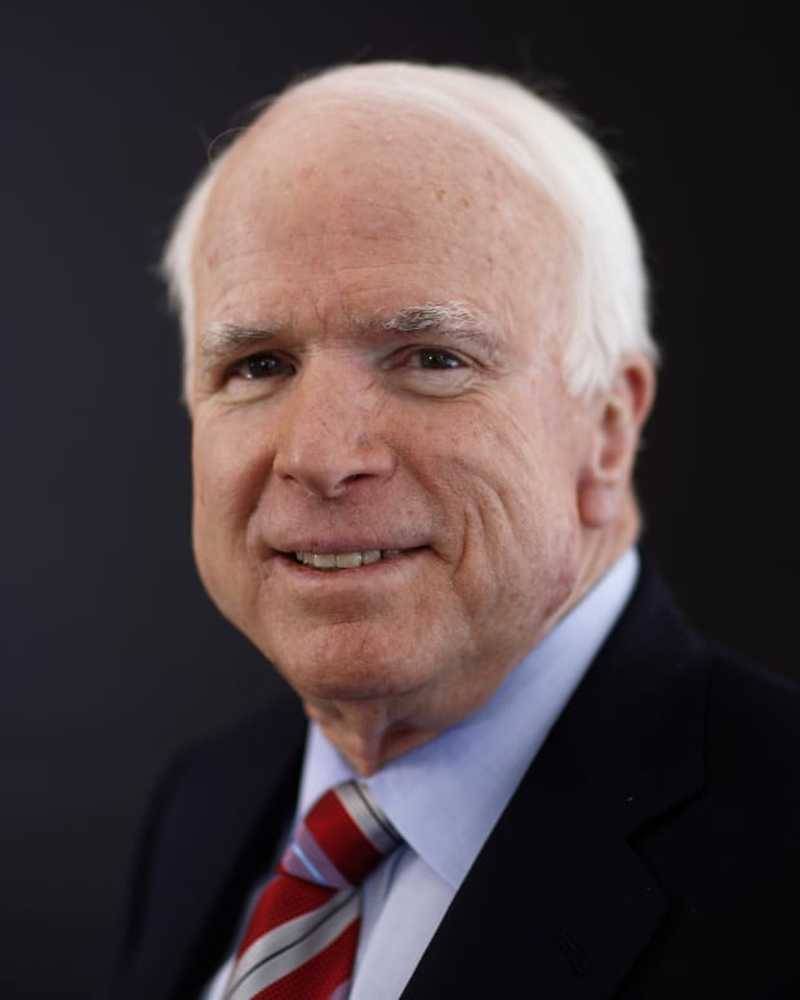 In het nieuws
In het nieuwsJohn McCain: War Hero, Senator, Maverick is overleden
De senator in Arizona zal lang worden herinnerd omdat hij trouw is gebleven aan zijn principes en het land heeft verkozen boven de politiek.
- Door Greg Timmons 21 juni 2019